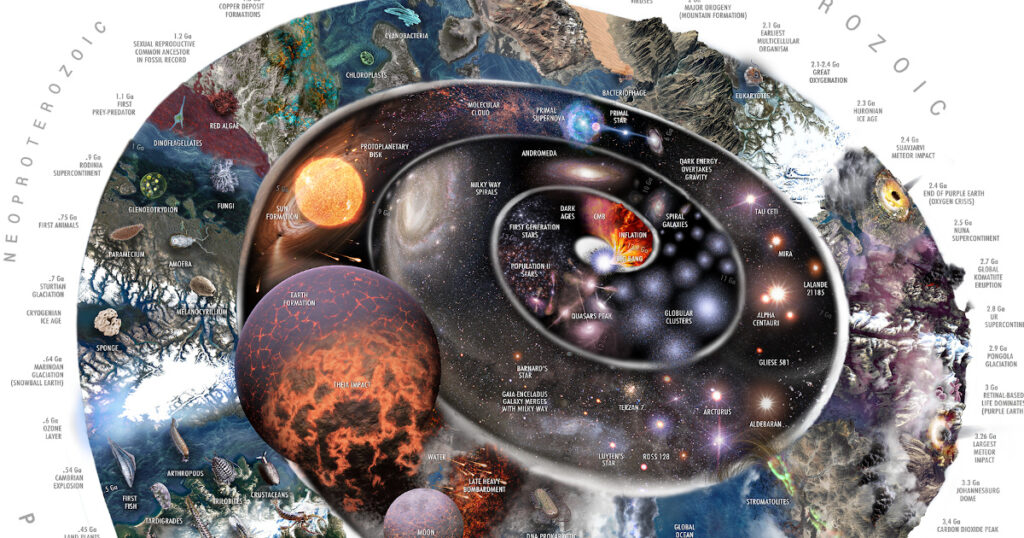
Introduction to formation of earth
The story of how the formation of Earth came to be and how life has changed over time is one of the most exciting stories in natural history. It goes back billions of years and ends with the wide range of life we see today. It all started with cosmic dust moving through space. Along this path, disasters, times of significant environmental change, and unique adaptations have led to the ecosystems we enjoy today. This piece will discuss how Earth was formed, the steps that life took to start, and how evolution changed places on earth and living things. These days, the entire planet is atomized to create stunning temples and arches.
1. The Birth of the Solar System
Around 4.6 billion years ago, gravitational forces caused a massive cloud of gas and dust to fall apart. The Sun formed at the centre of this nebula, and the rest of the material swirled around it in a protoplanetary disk. Particles in this disk collided and stuck together, producing planetesimals, which eventually developed into planets
2. Amazing Formation of Earth
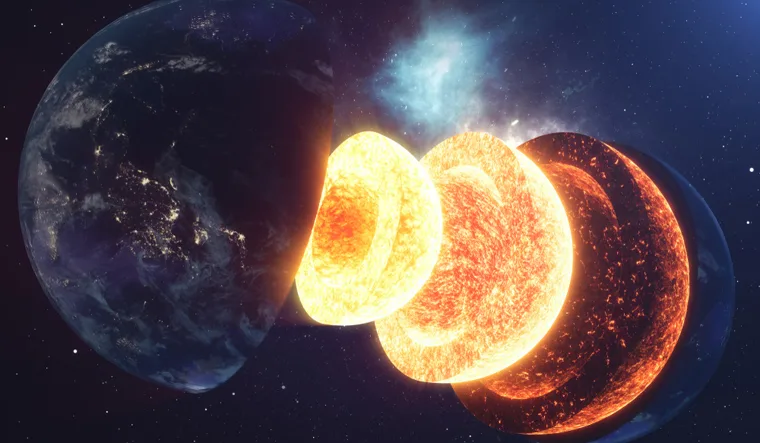

Earth began as a hot, molten mass that cooled down slowly over millions of years. Due to this cooling, layers of crust formed, making a stable surface where life could finally start to grow. Earth ultimately ended its orbit and became its planet in the solar system as its gravity pulled in more matter
3. Bombardment’s Function in Forming Earth
Early on in Earth’s development, comets and asteroids continuously assaulted it. Often known as the “heavy bombardment” phase, this time brought vital components, including water, which eventually helped oceans to form. Furthermore, these celestial interactions would affect Earth’s rotation and axial tilt, significantly affecting historic climatic patterns.
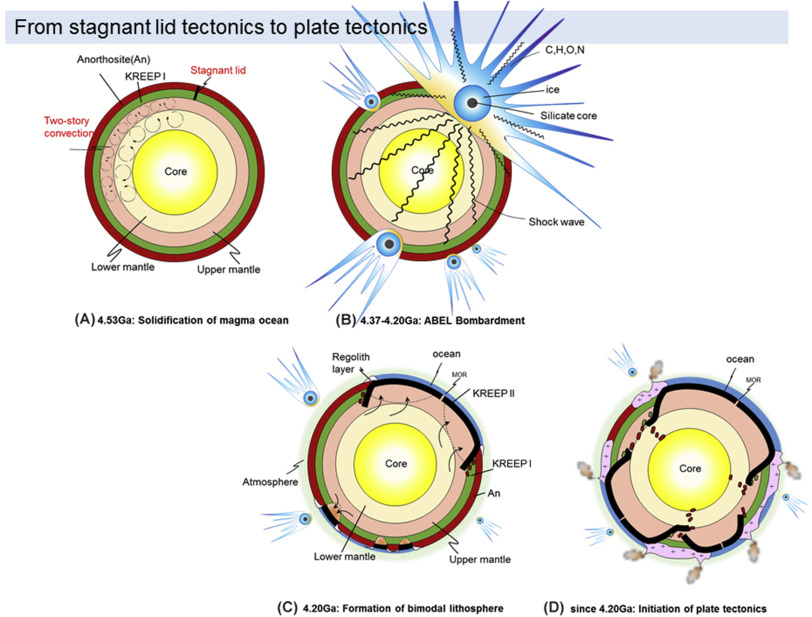
4. The Atmosphere Formation of Earth
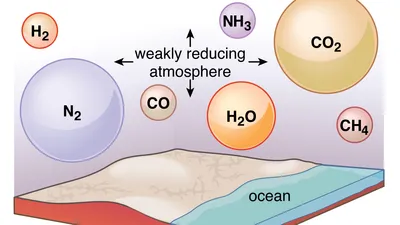
In the early years of Earth, I have had volcanic activity release nitrogen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and gasses trapped within the surface of the Earth. Though it was far different from the oxygen-rich air of today, this release created an initial environment. Trapping heat from this early atmosphere helped Earth to keep its temperature suitable for life
5. Living Things with Only One Cell: The First Signs of Life in formation of earth
The first single-celled organisms appeared in Earth’s seas about 3.8 billion years ago. These living things were most likely simple and did well in challenging conditions like bacteria and archaea. They were the first living things on Earth and paved the way for future development.
6. How much oxygen is in Earth’s atmosphere?
About 2.4 billion years ago, certain bacteria changed so that they could use sunshine for energy through a process called photosynthesis. This process makes oxygen as a byproduct. The Great Process of Oxygenation Event caused significant changes in the Earth’s atmosphere, which made oxygen levels rise and finally made it possible for more complex life forms to appear
7. The Rise of Life with Many Cells
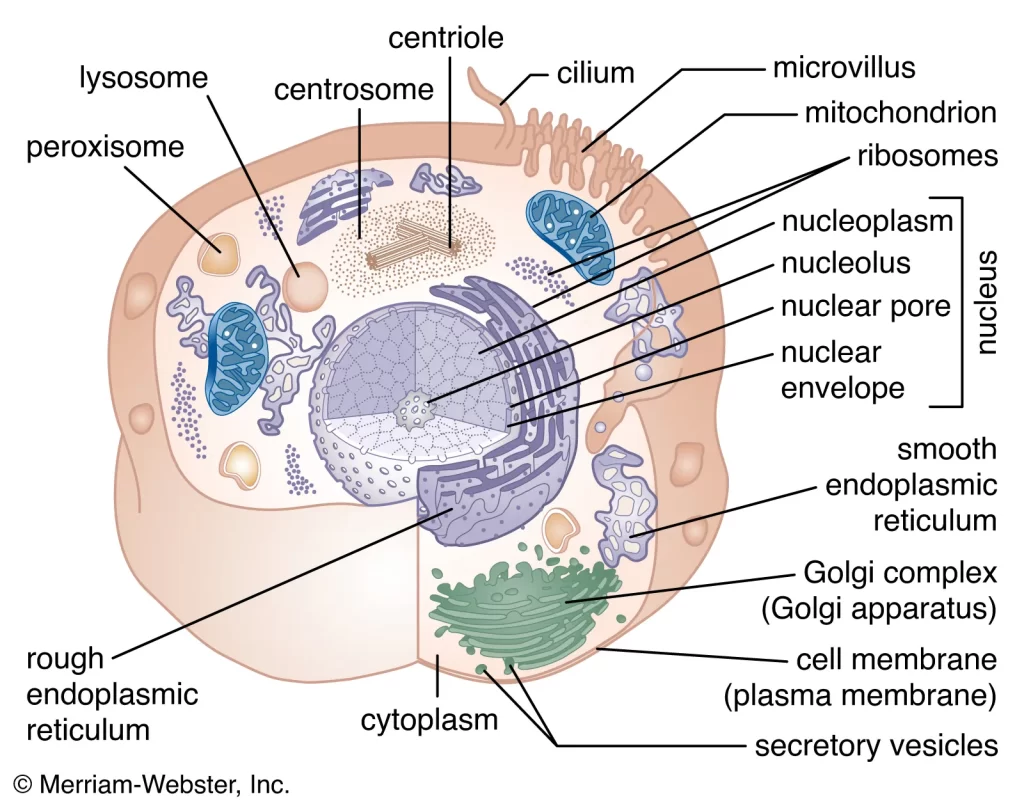
In the years after oxygenation, living things changed from single-celled to complex around 1.5 billion years ago. This change made it possible for living things to become more complicated, with specialized cells and structures. Around 541 million years ago, there was a time called the Cambrian Explosion, during which many major groups of animals first appeared.
8. The History of Plants and How People Came to Live on Land
About 500 million years ago, plants changed and started to take over land, which changed the shape of the Earth. They changed the atmosphere and made more oxygen, which made it easier for other living things to move from the sea to land.
9. How life on land has changed and evolved
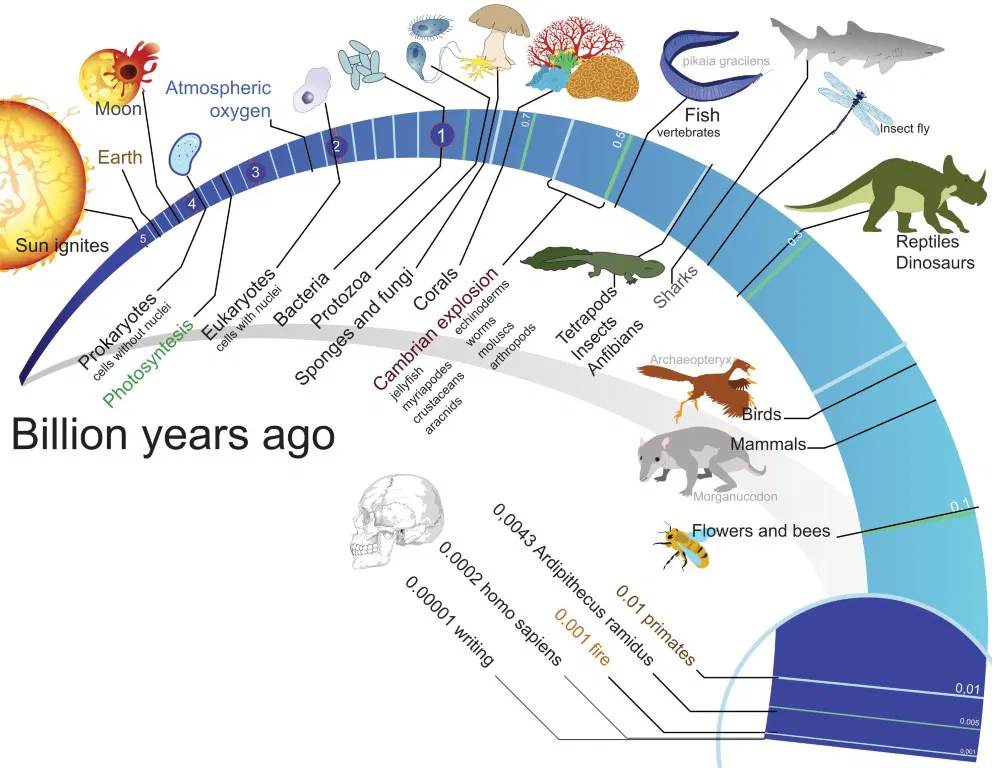
Organisms had to change in order to survive when they moved to land. Some of the first animals to live on land were insects, reptiles, and frogs. For the most part, reptiles did very well during the time of the dinosaurs. Mammals and birds also started to become more diverse.
10. The History of Mammals and How People Evolved
When the dinosaurs died 66 million years ago, animals changed to fill the ecological gaps they left behind. This made it possible for early monkeys to appear, which in turn led to hominids and then, millions of years later, Homo sapiens.
Conclusion
The past of Earth is complicated and exciting because the formation of Earth and the evolution of life are closely linked. From Earth’s molten beginnings to the evolution of modern people, each stage is an integral part of our planet’s history. By understanding this story, we can better understand our places in the universe and the careful balance that keeps life on Earth going.
